 Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System (HS) codes are product classification codes used by U.S. Customs and all other members of the World Customs Organization’s Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System to classify goods for customs purposes. The various digits of the numbered code specify categories, product types, and use case or materials. The multipurpose product codes, which have a standard structure, are used globally by more than 200 countries.
Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System (HS) codes are product classification codes used by U.S. Customs and all other members of the World Customs Organization’s Harmonized Commodity Description and Coding System to classify goods for customs purposes. The various digits of the numbered code specify categories, product types, and use case or materials. The multipurpose product codes, which have a standard structure, are used globally by more than 200 countries.
What Are HS Codes Used for?
Harmonized System codes are used throughout the export process to classify a product correctly and consistently. These classifications are often used in conjunction with country of origin certificates for calculating tariffs and customs duties. The product classification is important for calculating tariffs and customs duties, as tariffs and exceptions are based on the specifics of a product.
Companies may collect country of origin certificates and HS code data to maximize the use of free trade agreements and tariff exemptions, and avoid penalties. Country of origin certificates and HS codes are required to produce certifications for products covered by free trade agreements.
Example HS Code
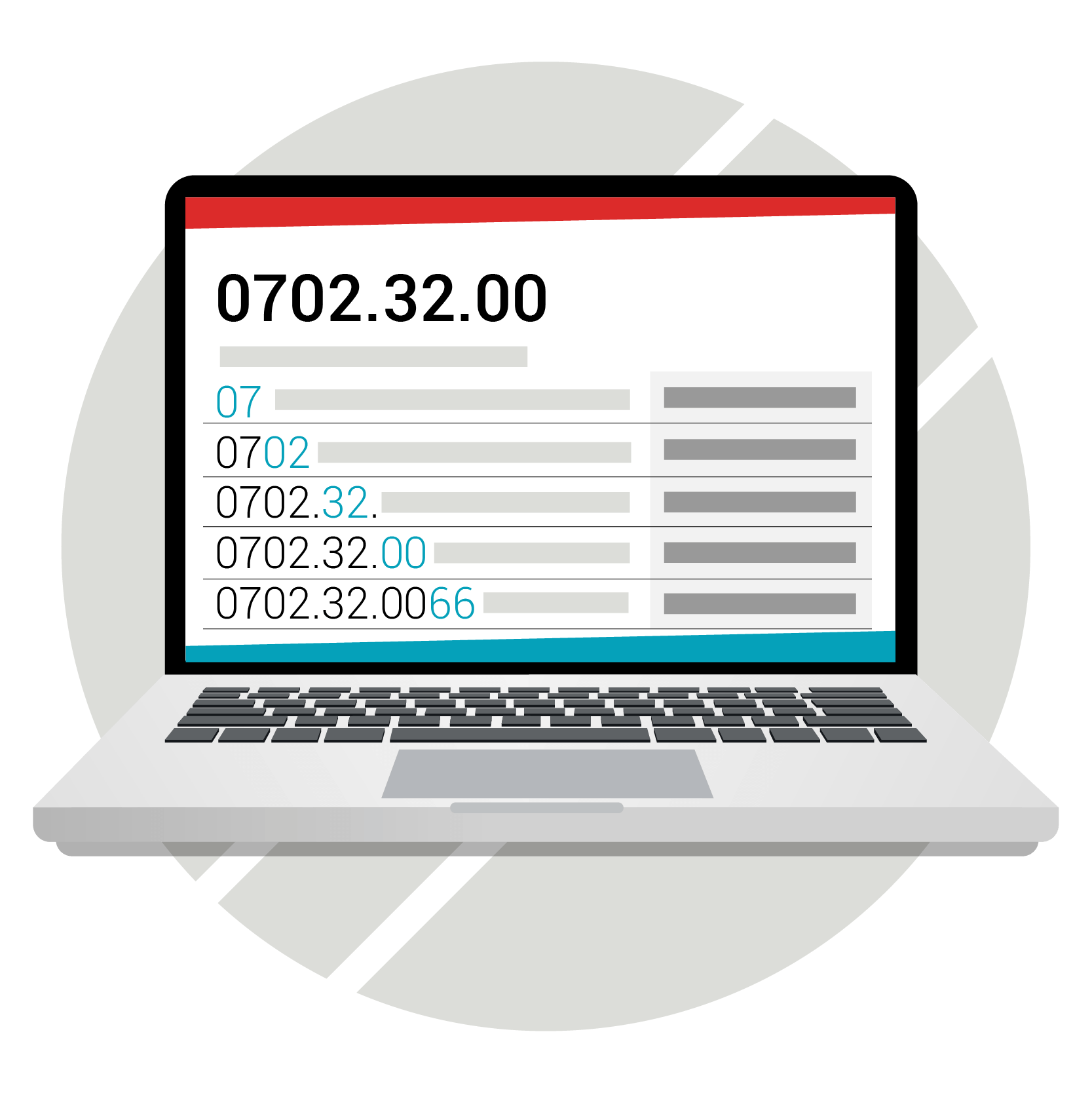
Each HS code describes a specific type of item. For example, a T-shirt’s HS code would depend on whether it was meant for an adult or infant, and what it is made of. A shirt with the HS code 6205.20 would be a men’s non-knitted or crocheted shirt, indicated by the 6205. The .20 indicates that the shirt is made of cotton.
Understand Trade Classification & Origin
Learn more about trade classification and origin, and how Assent can help you manage your trade compliance data.
Download Guide
Are HS Codes Used in the United States?

The United States adapts HS codes by adding an extra four digits to create a Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS or U.S.-HTS) code.
How Can Assent Help Manage HS Code & Trade Compliance Data?
Assent’s Trade Compliance and Origin Module:
- Allows users to cross-reference HTS codes with country of origin certificates.
- Provides evidence to claim free trade agreement status.
- Enables meaningful, streamlined data collection and harmonization of supplier classification.
- Creates a database of critical intelligence.
- Implements a reliable, consistent method for surveying suppliers, and verifying and cross-referencing information against tariff schedules to ensure data consistency.








